Table of Contents
What is a Pellet 3D Printer?
How does Pellet 3D Printing work?
What materials are used in Pellet 3D Printing?

Pellet 3D printing reviews versatile rhythm in material admiration. Plastic is dominant, sweeping across recognized options like PLA, ABS, or PETG. More novel materials like TPE, nylon, wood, and even metal composites join the fleet to affirmively gift the artist far-reaching dimensions of practical creativity.
Advantages of Pellet 3D Printing
Material Cost
Material Properties

Large-format Printing
Material Variety
Pellet 3D Printer excels in processing a wide range of thermoplastics and composites. This flexibility allows for experimenting with various pellets, including PA-CF, PA-GF, PC-CF, PLA, rPLA, PETG-GF, ABS, PS, GPPS, PP-GF, and more.
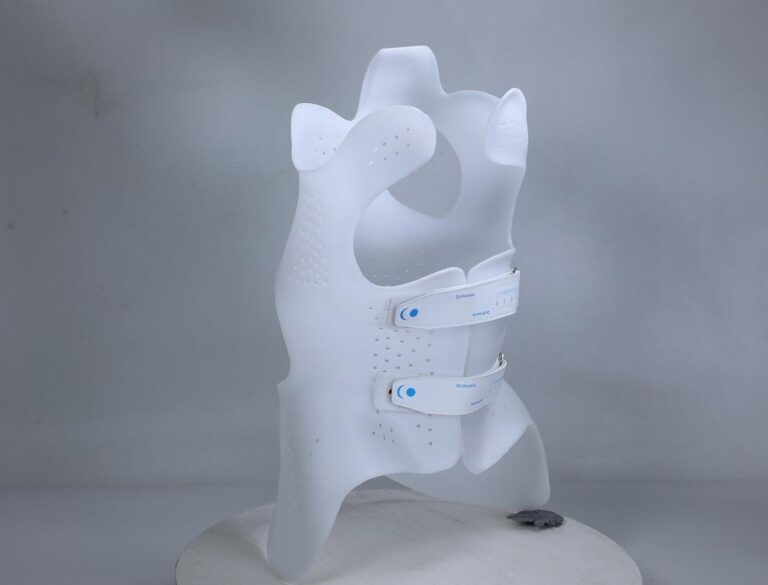
Pellet 3D Printing Common Applications
Low-volume Manufacturing
3D printing with pellets provides a useful tool for meeting specialized, low-volume needs. It promotes a forward-thinking approach to developing customized solutions, enhancing client satisfaction by focusing on their unique requirements.
Prototyping
From faster prototyping to better support tooling to economical customization and production, additive technology offers time and cost efficiencies while getting products to market faster. Validate ideas faster to arrive at the optimal design before investing in expensive production tooling.
Mold Tooling
From employing vacuum forming to utilizing composite molds, pellet 3D printing offers a quick, cost-effective, and robust method for tooling. Our technology permits manufacturers to produce cost-efficient, custom injection molds using 3D-printed tooling. This allows designers and engineers to conduct more frequent and precise tests of their product,speeding up the product development

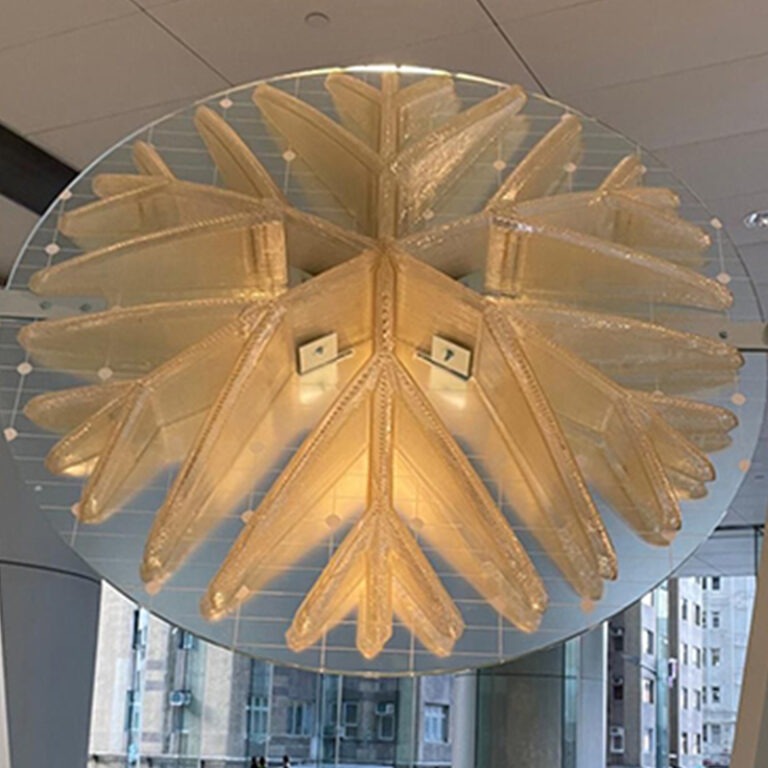
Artistic Installations
The layer-by-layer construction of objects in 3D printing results in unprecedented geometric freedom. Artists now have the capability to create designs with 3D printers, unconcerned about the feasibility of their production.
Whatever can be imagined can be printed, encompassing fields like artistic installations, architecture, or sculpture. Pellet 3D printing technologies further allow for the large-scale printing of fine art and sculptures.
PioCreat Pellet 3d printer
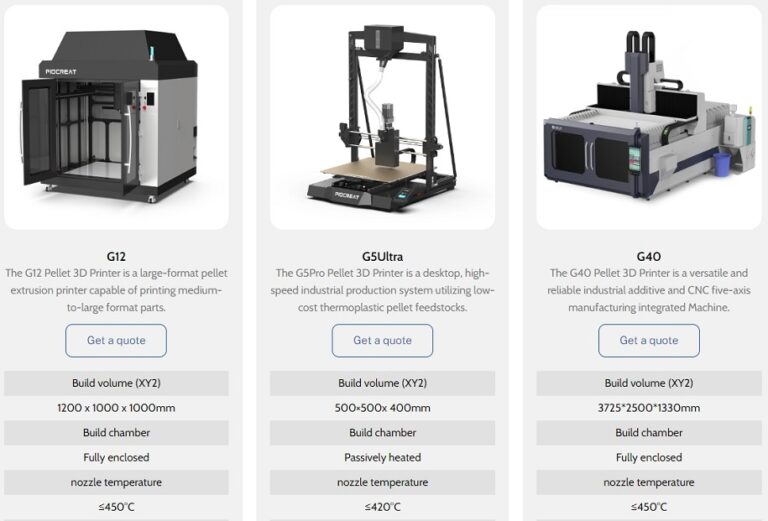
PioCreat 3D has recently launched three types of pellet 3D Printer, marking a substantial enhancement in pellet printing technology. By exploring these innovative machines, it becomes evident how they modernize and accelerate the world of 3D printing:
Reduced Lead Times
These printers significantly speed up production—with speeds up to ten times faster than traditional filament extrusion 3D printing. The G5Ultra boasts a maximum extrusion volume of 0.8kg per hour, the G12 offers up to 3kg per hour, and the G40 leads the pack with an impressive 25kg per hour, in stark contrast to the 40g to 50g per hour rate of conventional FDM printers. This boost in speed translates to drastically shortened project timelines.
Enhanced Material Quality
PioCreat’s FGF (Fused Granular Fabrication) technology melts plastic pellets directly, which not only preserves the inherent properties of the plastics but also improves the adaptability towards various printing materials. This results in lower material costs and markedly better performance of the parts. Moreover, it eliminates the frequent issue of filament breakage seen in traditional FDM printing. By using original quality materials, printer throughput is optimized and the physical properties of crafted components are significantly elevated.
Environmental Sustainability
The printers encourage environmentally responsible practices by utilizing both pellets and shredded recycled plastics. This not only promotes sustainable manufacturing but also substantially reduces material costs by more than 60%. As a versatile solution, this method facilitates an economically and environmentally beneficial approach across a broad array of applications.
Cost Efficiency
Lastly, using pellet extrusion greatly curtails expenses, where costs are approximately ten times lower compared to filament-based methods. In addition to omitting a processing step in filament creation, the widespread availability and bulk utilization of pellets in industries like injection molding ensure affordability due to a more competitive market.
To Summarize
Pellet 3D printers offer cost-efficiency by using cheaper, raw plastic pellets instead of filaments, aimed at large-scale productions. Their high-throughput capability enables faster printing, while recyclability ensures waste minimization for sustainability. Common applications include automobile, furniture, and prototyping sectors, driving innovations by streamlining production or creating complicated designs.