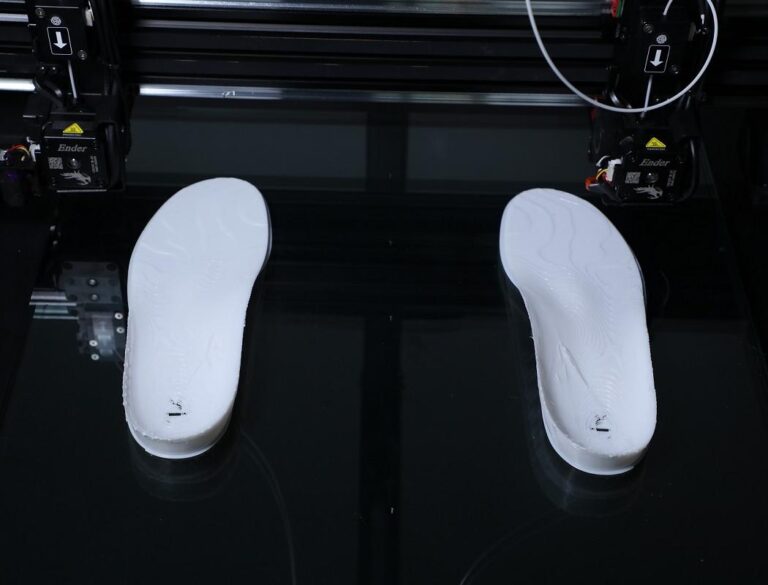
In today’s fast-paced industries, time-to-market is crucial, and companies need efficient ways to test, validate, and refine their products. This is where rapid prototyping plays a significant role. It allows businesses to create physical models of their designs quickly and cost-effectively, ensuring faster iterations and better final products. With the advent of 3D printing, rapid prototyping has become even more accessible and versatile, benefiting a wide range of industries. In this blog, we will explore what rapid prototyping is, how it works, its types, and its applications across industries.

What is Rapid Prototyping?
Rapid prototyping refers to the process of quickly creating a physical model or prototype of a product or part to visualize, test, and validate the design before it goes into full-scale production. The goal of rapid prototyping is to speed up the product development process, enabling engineers and designers to test ideas and iterate on their designs more efficiently.
Rapid prototyping is widely used in product development across industries like aerospace, automotive, healthcare, and consumer electronics. By creating prototypes quickly, businesses can identify design flaws early, experiment with different materials, and ultimately produce higher-quality products.
How Does Rapid Prototyping Work?
Rapid prototyping typically starts with a digital design created using CAD (computer-aided design) software. Once the design is ready, it’s fed into a 3D printer or other prototyping machine that transforms the digital model into a physical object. The process usually involves additive manufacturing techniques, where materials like plastic or metal are added layer by layer to build the prototype.
The key advantage of rapid prototyping is its ability to produce functional models within hours or days, depending on the complexity of the design. This allows teams to review and refine their designs in real-time, making it possible to go through multiple iterations before finalizing the product.
What Are the Different Types of Rapid Prototyping?
Rapid prototyping can be categorized into several types, depending on the purpose of the prototype. Each type serves a different function within the product development process:
Functional Prototyping
Functional prototyping involves creating a prototype that closely resembles the final product in terms of functionality, materials, and design. This type of prototype is often used to test how the product will perform in real-world scenarios. Functional prototypes are essential for validating design decisions and ensuring that the product will meet the required specifications and performance standards.
Product Validation
Product validation prototypes are used to verify that the design meets all necessary requirements, such as aesthetic appeal, usability, and functionality. These prototypes are typically used during the final stages of the product development process to ensure that the product will perform as intended and that all design features are correct.
Engineering Prototypes
Engineering prototypes are created to test the engineering aspects of a design, such as the structural integrity, durability, and mechanical performance of a product. These prototypes are often subjected to rigorous testing to ensure that the product can withstand the conditions it will encounter during use. Engineering prototypes are crucial for industries like aerospace and automotive, where safety and reliability are paramount.
Industries Leveraging 3D Printing for Rapid Prototyping
Rapid prototyping has gained widespread adoption across various industries due to the speed, precision, and cost-efficiency it offers. Here are three industries where rapid prototyping with 3D printing is making a significant impact:
Aerospace
In the aerospace industry, 3D printing for rapid prototyping allows engineers to create highly complex parts, such as turbine blades and structural components, to test their functionality before production. The ability to quickly produce lightweight yet durable prototypes is critical for improving fuel efficiency and safety in aircraft.
Automotive
In the automotive industry, rapid prototyping is used to design and test components such as engine parts, dashboards, and chassis elements. With 3D printing, automotive manufacturers can quickly iterate on designs, optimize aerodynamics, and test the fit and function of parts before moving to mass production. This reduces both time and costs in the production cycle.
Education
In the education sector, rapid prototyping provides students and researchers with hands-on experience in product development. Universities and technical institutions use 3D printers to create prototypes for academic projects, fostering creativity and innovation in engineering and design fields.
Benefits of Rapid Prototyping with 3D Printing
Using 3D printing for rapid prototyping offers several advantages that make it a preferred method in various industries:
Shorter Lead Times
Traditional prototyping methods can take weeks to produce a prototype, but 3D printing drastically reduces lead times by allowing manufacturers to create prototypes in a matter of hours or days. This speeds up the product development cycle and allows for quicker decision-making.
Cost Efficiency
Rapid prototyping with 3D printing is cost-effective because it eliminates the need for expensive tooling and molds. Companies can produce multiple iterations of a design without incurring high costs, making it an ideal choice for low-volume production and iterative testing.
Ease of Use
Modern 3D printing technologies are user-friendly and accessible, making it easier for designers and engineers to produce prototypes in-house. This reduces the reliance on external suppliers and gives companies more control over the prototyping process.
Same-Platform Prototyping and Production
One of the key benefits of 3D printing is that the same machine can be used for both prototyping and production. Once a design is validated through prototyping, the same 3D printer can be used to produce the final product, ensuring consistency and quality throughout the production process.
High-Performance Materials for Rapid Prototyping
Choosing the right material is crucial for producing high-quality prototypes that closely resemble the final product. Here are some of the most commonly used materials in 3D printing for rapid prototyping:
PA+CF
PA+CF (Polyamide with Carbon Fiber) is a carbon fiber-reinforced polyamide material that offers high strength, rigidity, and thermal resistance. It is easy to print, resistant to warping, and can withstand temperatures up to 150°C. This material is ideal for industrial applications that require durability and high performance.
ABS+CF
ABS+CF is a carbon fiber-reinforced version of ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene). This material combines the flexibility of ABS with the strength of carbon fiber, making it a great choice for producing functional prototypes that require impact resistance and durability.
PC+CF
PC+CF (Polycarbonate with Carbon Fiber) is known for its impact resistance and mechanical strength. It is commonly used in industries like automotive and aerospace, where parts need to withstand high stress and harsh conditions.
PETG-GF
PETG-GF is a glass fiber-reinforced version of PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol). This material contains 10% glass fiber and offers excellent printability and cost-effectiveness. It is often used in mid-area additive manufacturing for creating prototypes that require strength and durability.
Best 3D Printers for Rapid Prototyping
To achieve high-quality prototypes, using the right 3D printer is essential. Here are two of the best 3D printers for rapid prototyping:
G5Ultra Pellet 3D Printer
The G5Ultra Pellet 3D Printer is a desktop-sized industrial production system designed for rapid prototyping. With a build volume of 500×500×400mm, this printer offers high-speed production using low-cost thermoplastic pellets.
Key features include:
- Nozzle temperature up to 400°C
- Rapid heating of the hot bed up to 120°C
- Screw extruder design for improved material flow
- Compatibility with a wide range of materials
G12 Pellet 3D Printer
For larger-scale rapid prototyping, the G12 Pellet 3D Printer offers a massive 1200×1000×1000mm build volume, making it ideal for producing large-format prototypes.
Key features include:
- 450°C nozzle temperature
- 120°C rapid heating of the hot bed
- High flow screw extrusion for efficient material handling
- Robust servo motor for precision printing
Final Thoughts
Rapid prototyping with 3D printing has revolutionized the way industries approach product development. From speeding up the design process to reducing costs and improving product quality, the benefits of 3D printing for rapid prototyping are undeniable. With high-performance materials and advanced 3D printers like the G5Ultra and G12 Pellet 3D Printers, companies can now bring their ideas to life faster and more efficiently than ever before.