3D Printed Wall Climbing Magnetic Device with G5 Ultra
piocreat3d
on
May 29, 2025
At the intersection of creativity, engineering, and cutting-edge fabrication lies a compelling experiment from Canadian content creator Tyler Csatari, who boasts an audience of 2.65 million followers. His recent project—a wall climbing magnetic device—showcases not only his inventive spirit but also the powerful capabilities of PioCreat’s G5 Ultra Pellet 3D Printer.
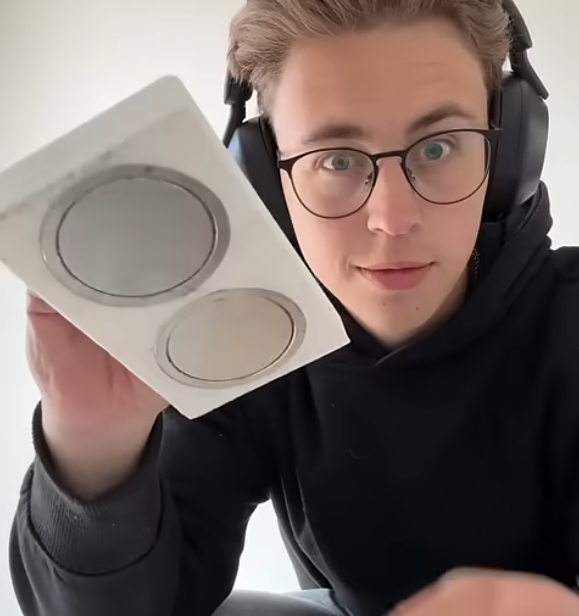
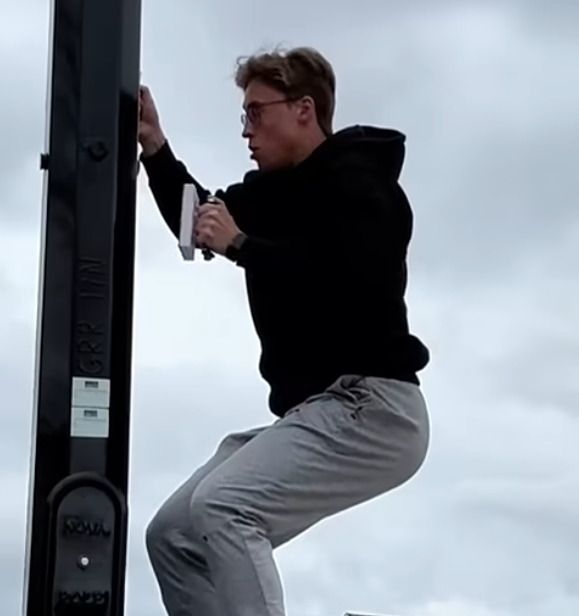


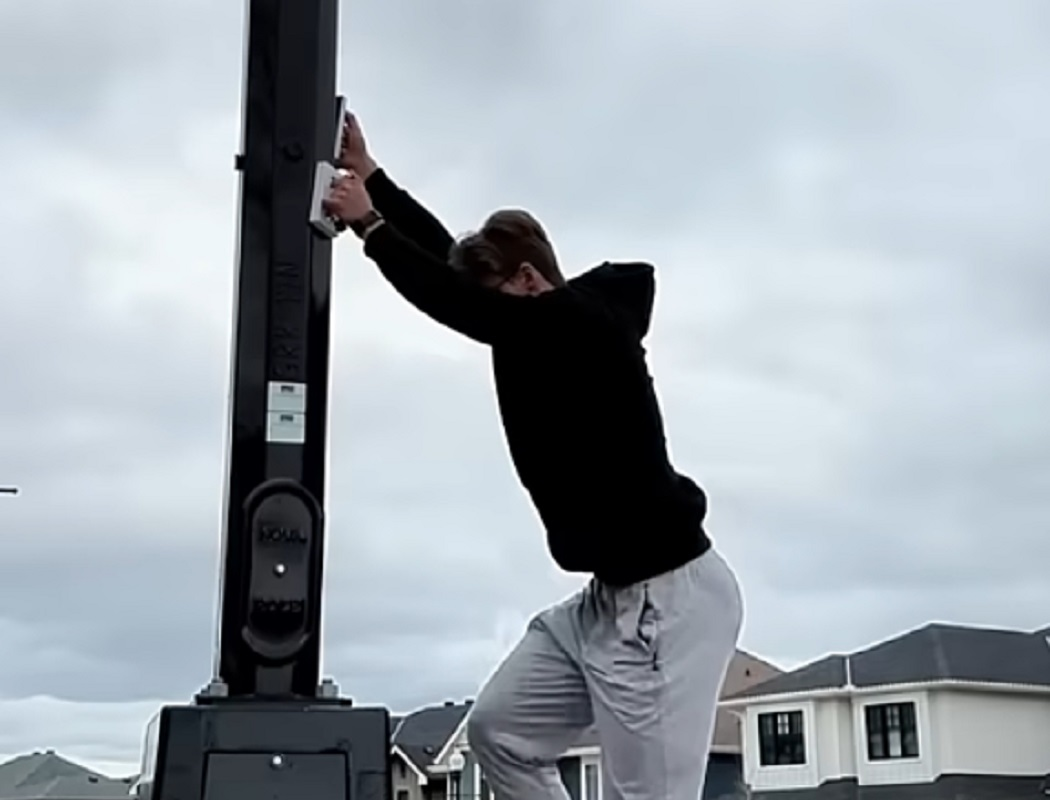
In this exciting build, Tyler set out to test a set of industrial magnets rated to support up to 400 pounds with the goal of creating a functional wall-climbing tool. However, during initial trials, he discovered a critical flaw: the magnets slipped easily on surfaces, failing to provide the necessary grip to support his weight.
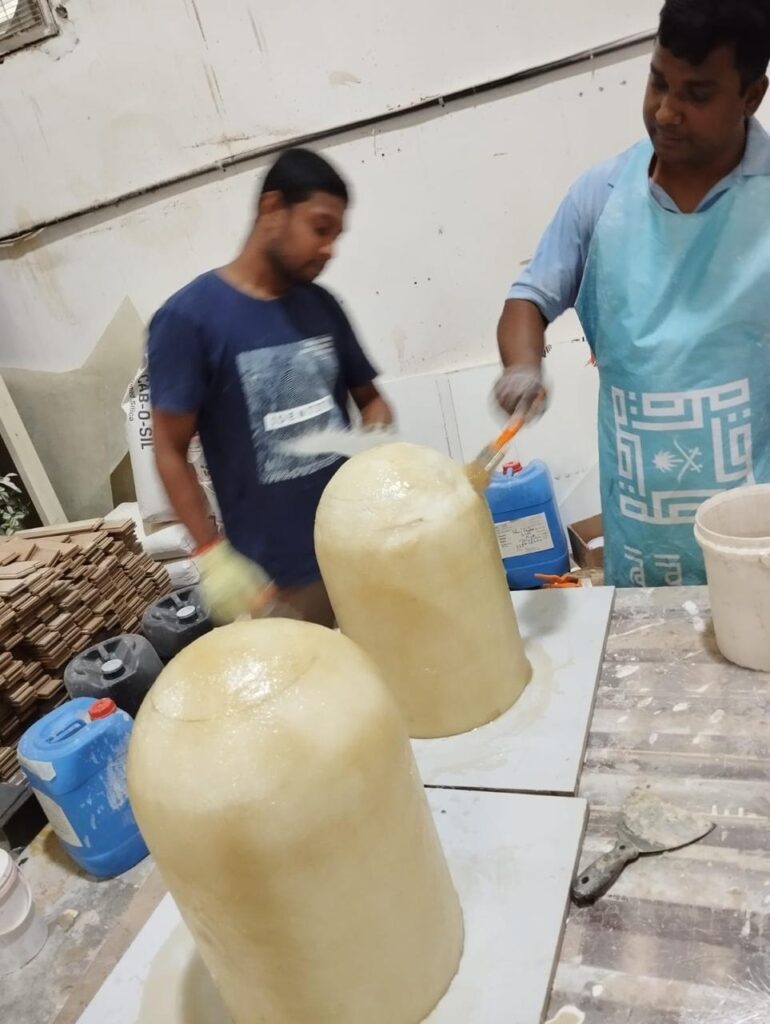
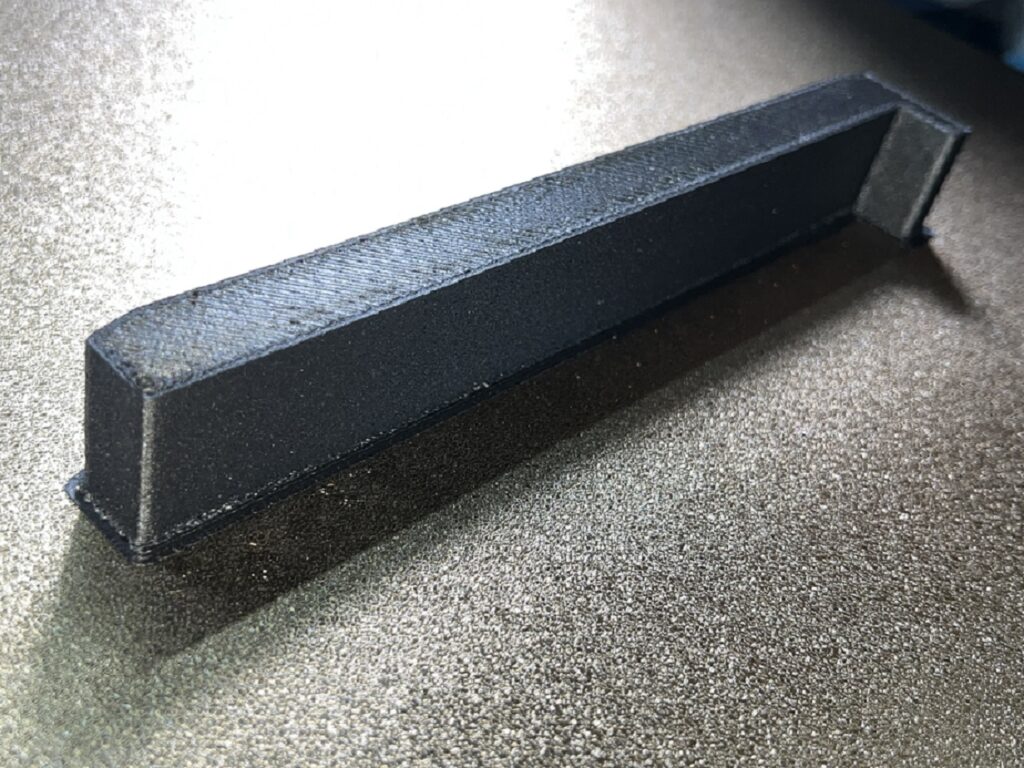
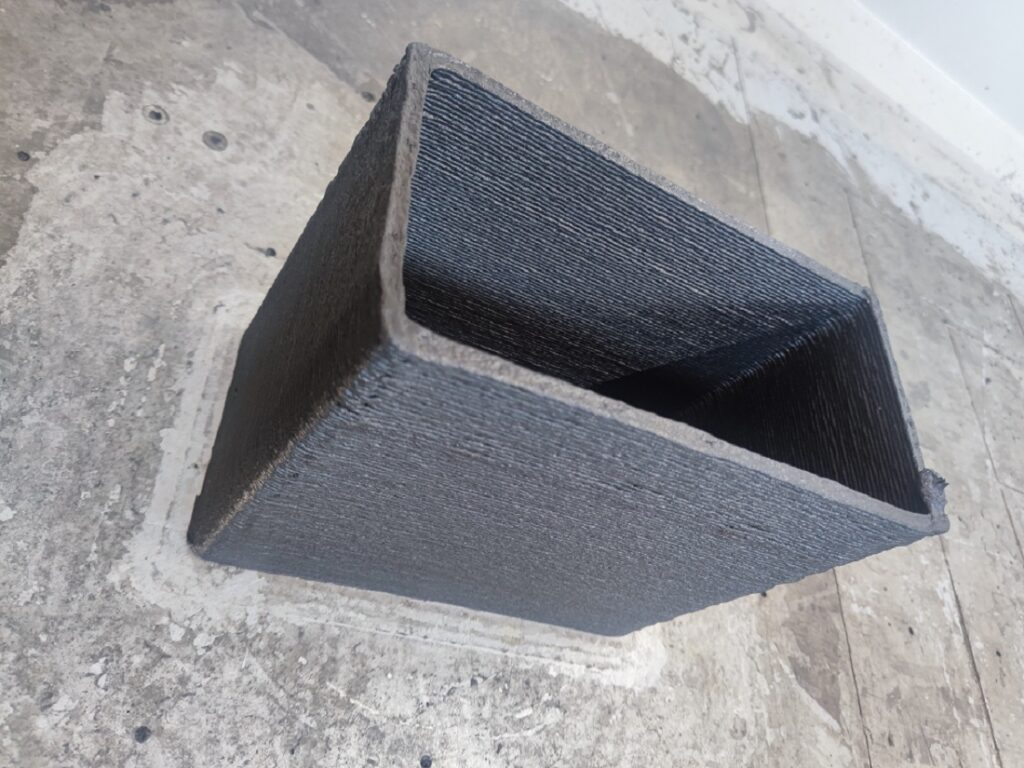
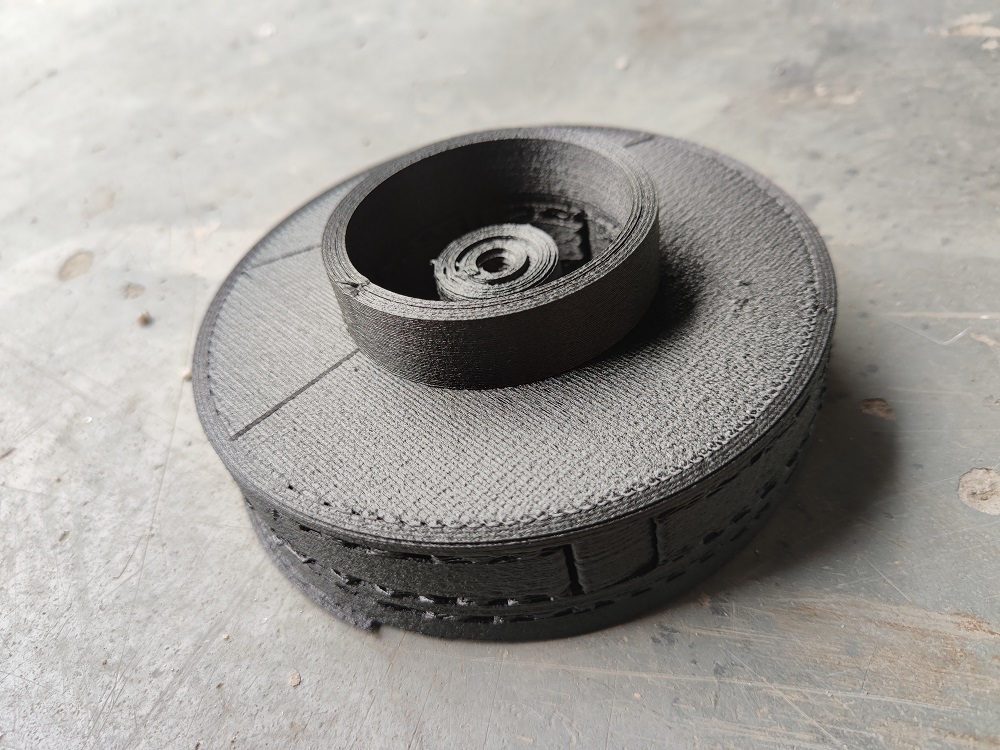
To solve this, Tyler turned to additive manufacturing. Leveraging the G5 Ultra’s FGF (Fused Granulate Fabrication) 3D printing technology, he began printing parts with a custom material blend—including iron powder and flexible rubber pellets—to create components that were both magnetic and non-slip.
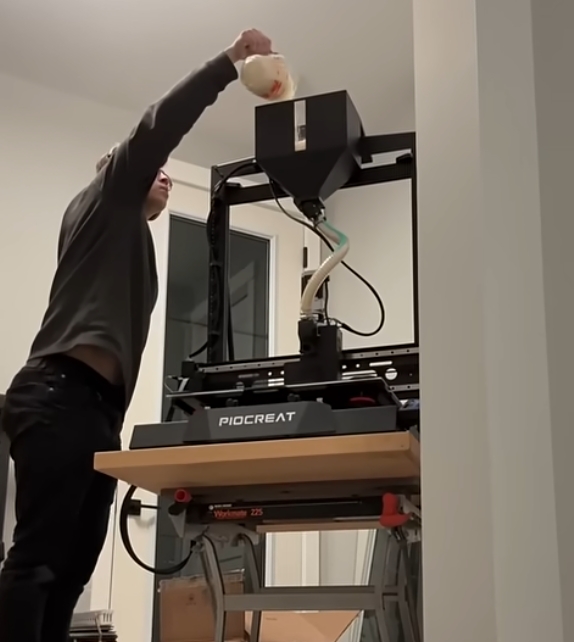
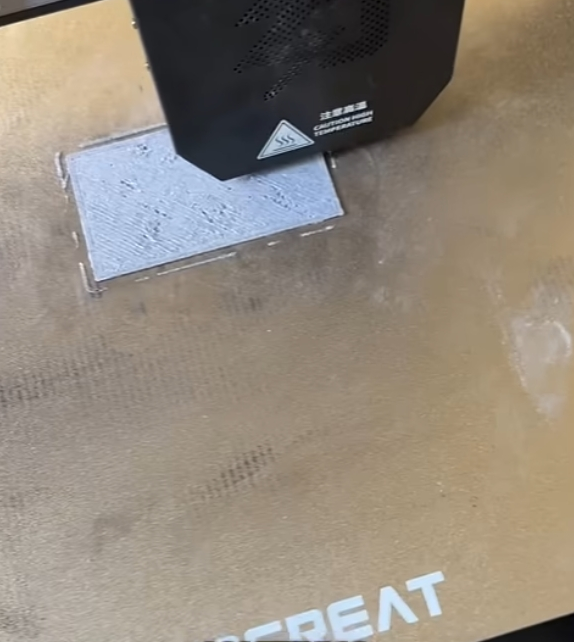


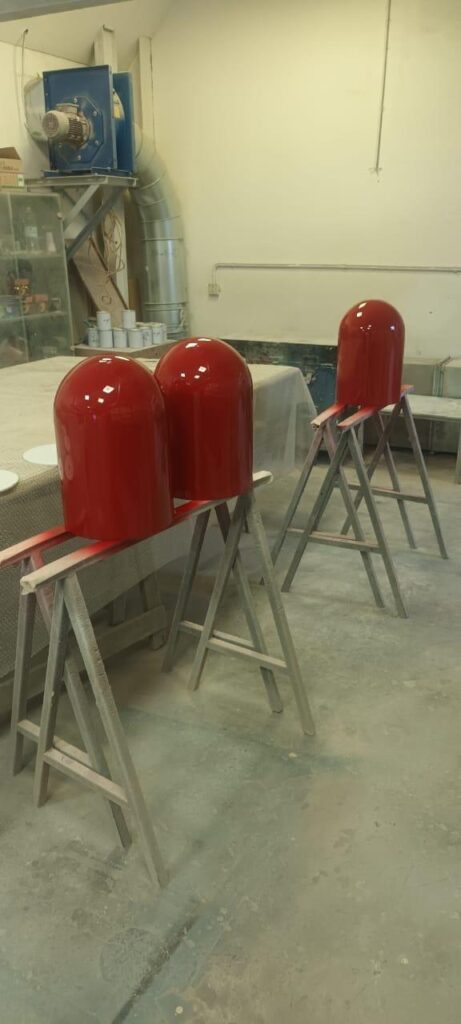
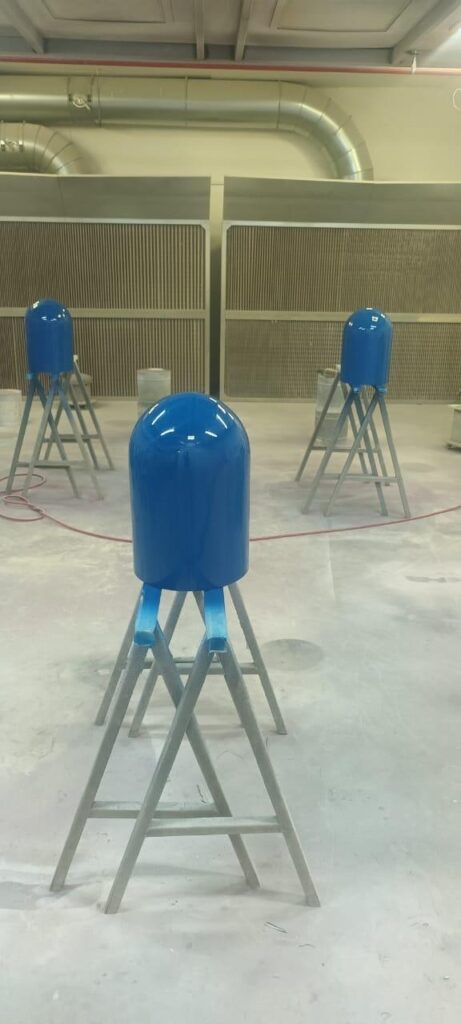
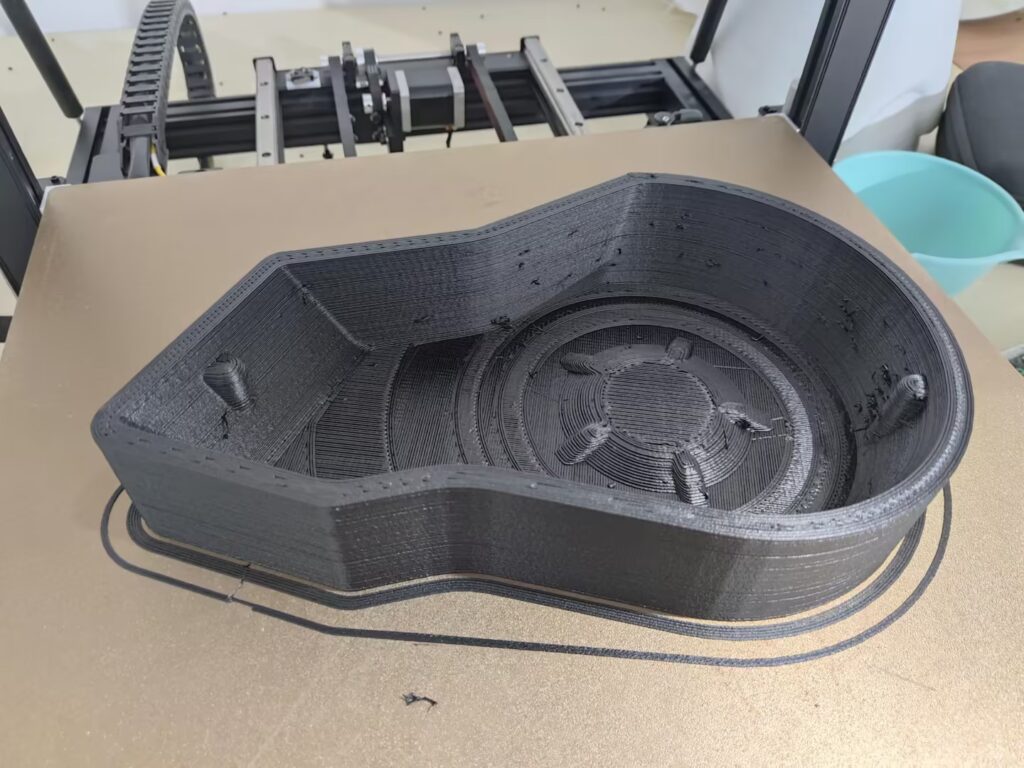
Throughout the project, he faced several engineering challenges. Structural fractures in early prototypes forced him to repeatedly refine the design. But thanks to the G5 Ultra’s material compatibility, large build volume (500×500×400 mm), and screw extruder system, Tyler was able to iterate quickly, pushing the limits of functionality with each version.
Ultimately, his perseverance paid off. The final result was a full “wall climbing suit” equipped with magnet-enhanced grips for both hands and feet. The combination of material innovation and rapid prototyping enabled by the G5 Ultra allowed him to move from concept to a working prototype within a remarkably short timeframe.
This case study highlights more than a viral video—it demonstrates the real-world potential of pellet 3D printing in functional prototyping, particularly in combining multi-material composites to solve performance-based problems.