3D Printing Insole Customization: A Smarter Approach to Orthotic Solutions
piocreat3d
on
June 4, 2025
The orthotics industry is undergoing a rapid transformation. As the demand for personalized, high-performance foot care rises, 3D printing is proving to be a powerful tool in delivering efficient, accurate, and scalable solutions for custom orthotic insoles. Leveraging technologies like advanced gait analysis, foot scanning, and proprietary OEM production workflows, clinics and manufacturers can now deliver tailored insole solutions faster, more affordably, and with superior consistency.
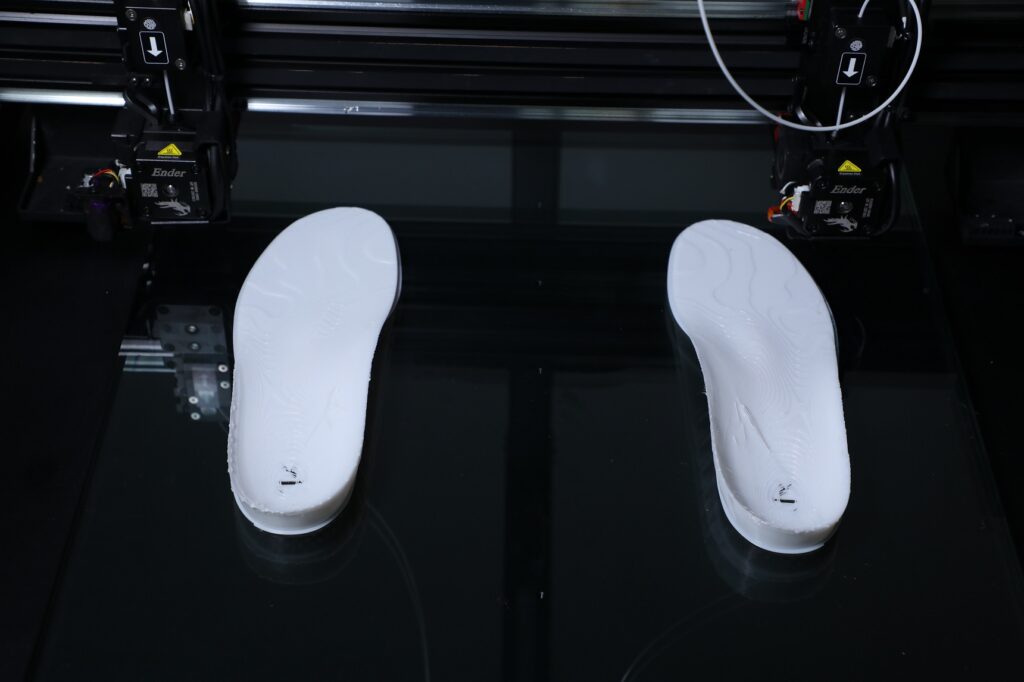

The Need for Customization in Foot Orthotics
No two feet are exactly alike. Variations in foot arch, gait, pressure points, and structure mean that one-size-fits-all insoles often fall short—particularly for patients with specific needs related to posture, pain management, or rehabilitation. Traditional methods of custom insole production can be slow, expensive, and prone to inconsistencies.
That’s where 3D-printed orthotic insoles change the game. They offer precision, adaptability, and repeatability—hallmarks of any high-quality medical device.
From Foot Scan to Finished Product: How the Process Works
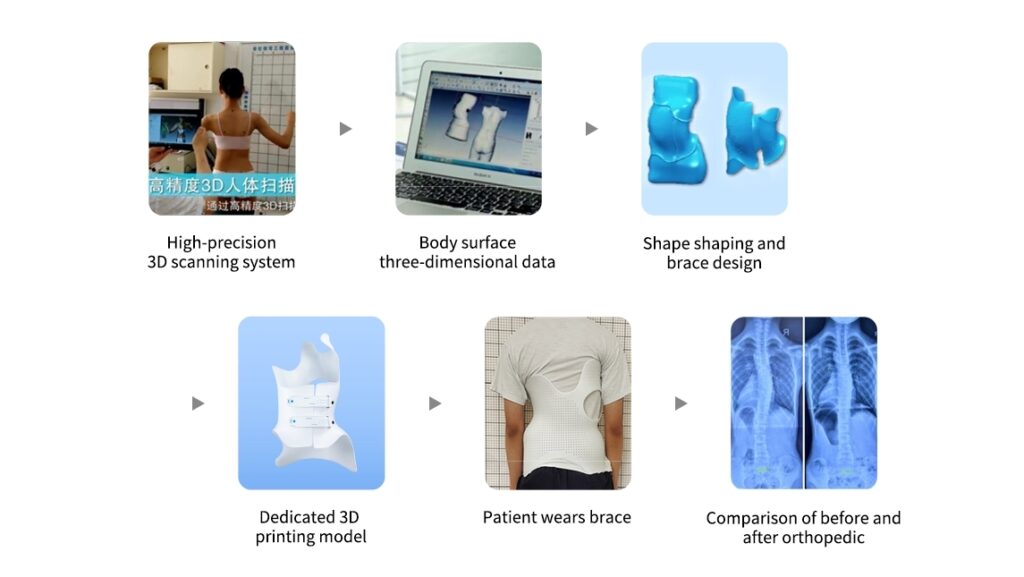
Delivering a custom-fit insole involves more than just printing a shape. It requires a full-stack approach—from biometric data capture to final finishing—each step designed to ensure clinical-grade outcomes.
1. Gait Analysis
Dynamic gait analyzers capture how a person walks, highlighting imbalances or asymmetries that could contribute to foot pain, knee issues, or back problems.
2. 3D Smart Foot Scanning
Devices like the FS A003 and FS B001 generate highly accurate 3D models of the foot. The FS A003 captures millimeter-level detail in just 5–10 seconds, while the FS B001 delivers ultra-fast, ±2–3mm precision in as little as 1.5 seconds. These scanners are especially valuable in clinical settings where time and accuracy are critical.
3. Data Analysis
Using software to analyze pressure distribution, arch type, and structural anomalies, clinicians can make data-driven decisions on support zones, material density, and geometry.
4. Custom Insole Design
With this rich dataset, CAD tools help generate a digital insole model tailored to the individual’s foot shape and biomechanical needs.
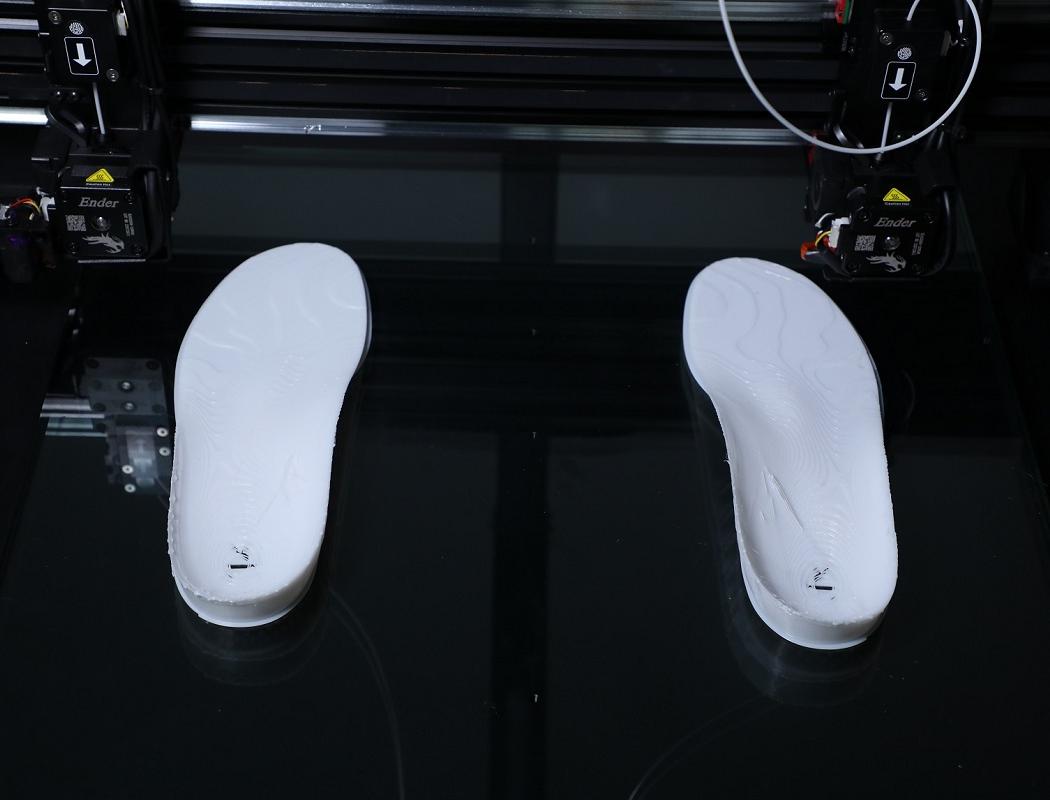
5. 3D Printing
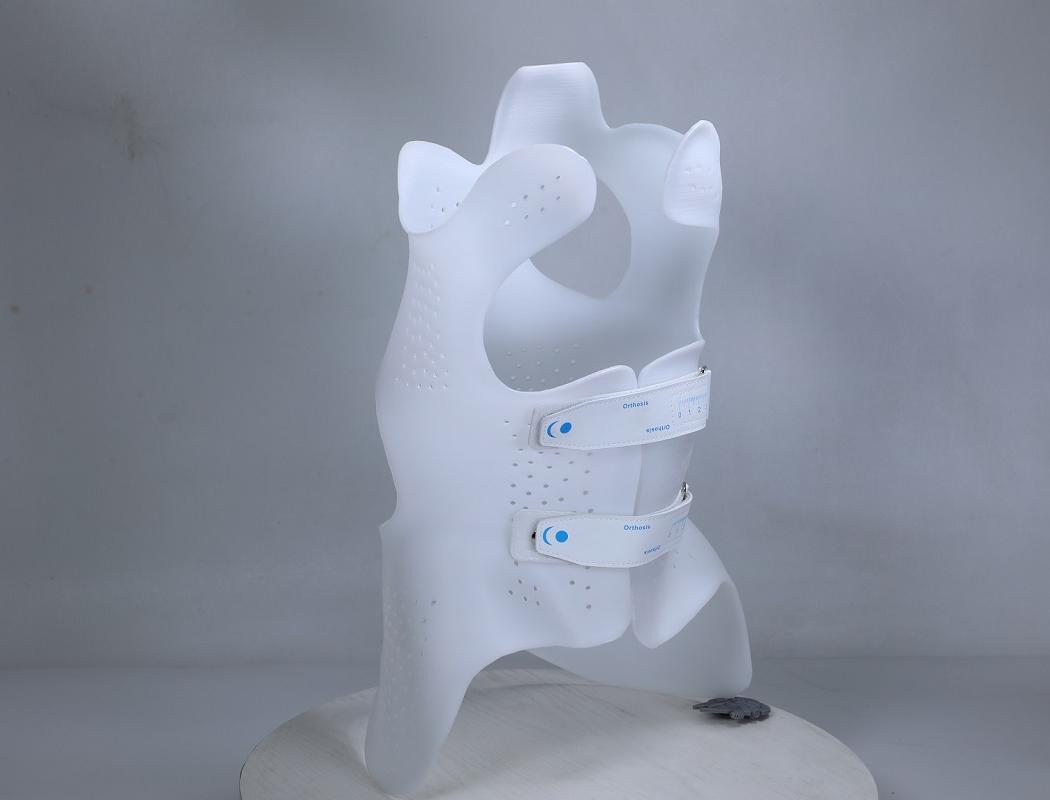
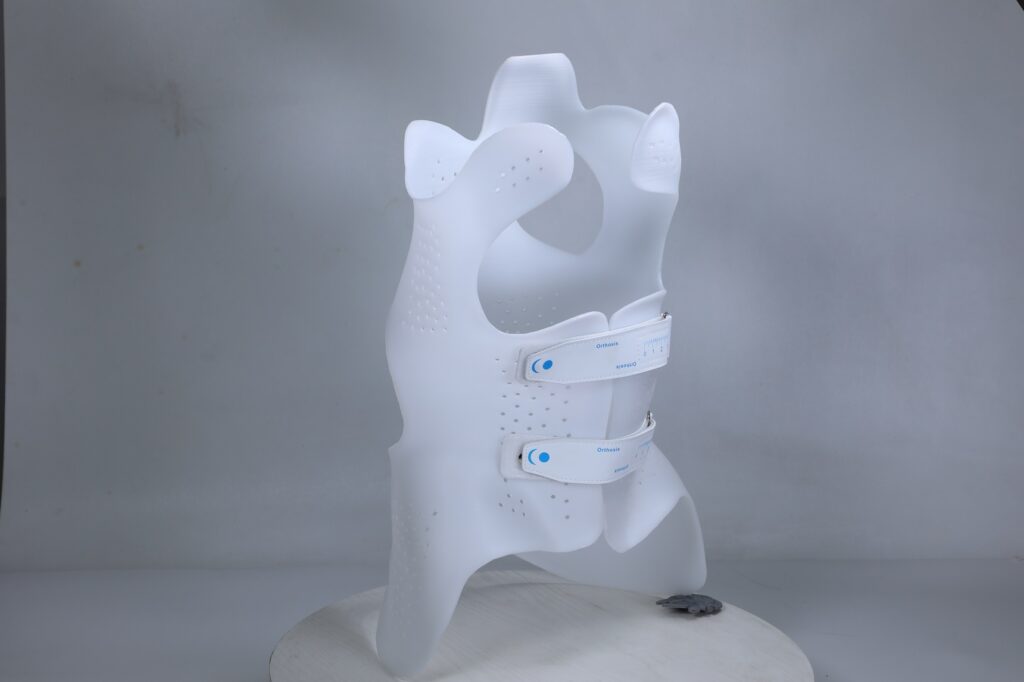
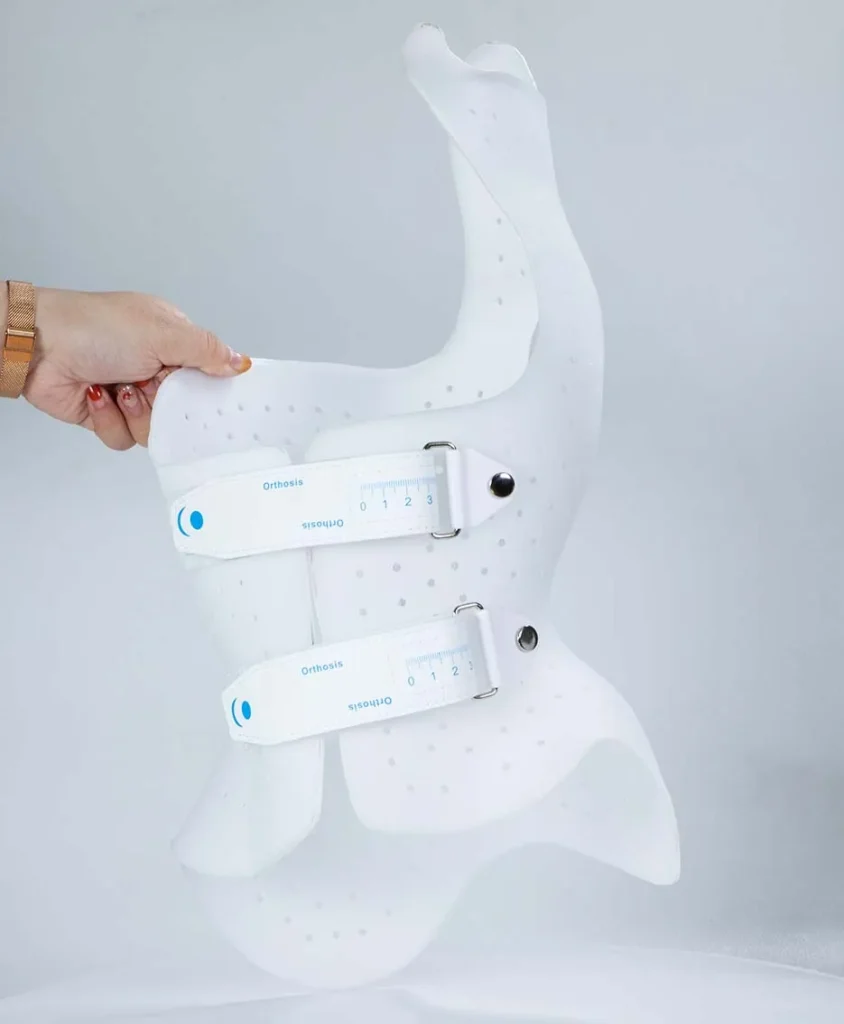
Custom insole models are printed using specialized FDM printers like the IPX2. This machine features independent dual nozzles, allowing simultaneous printing with flexible and rigid materials—ideal for combining comfort with structural support.
6. Insole Veneer Production
Aesthetic and functional veneers—customizable by color, finish, or antimicrobial properties—are added to match the patient’s lifestyle or medical requirement.
7. Polishing and Finishing
Final polishing ensures comfort, accuracy in fit, and wearability. Each pair is finished to clinical-grade standards before delivery.
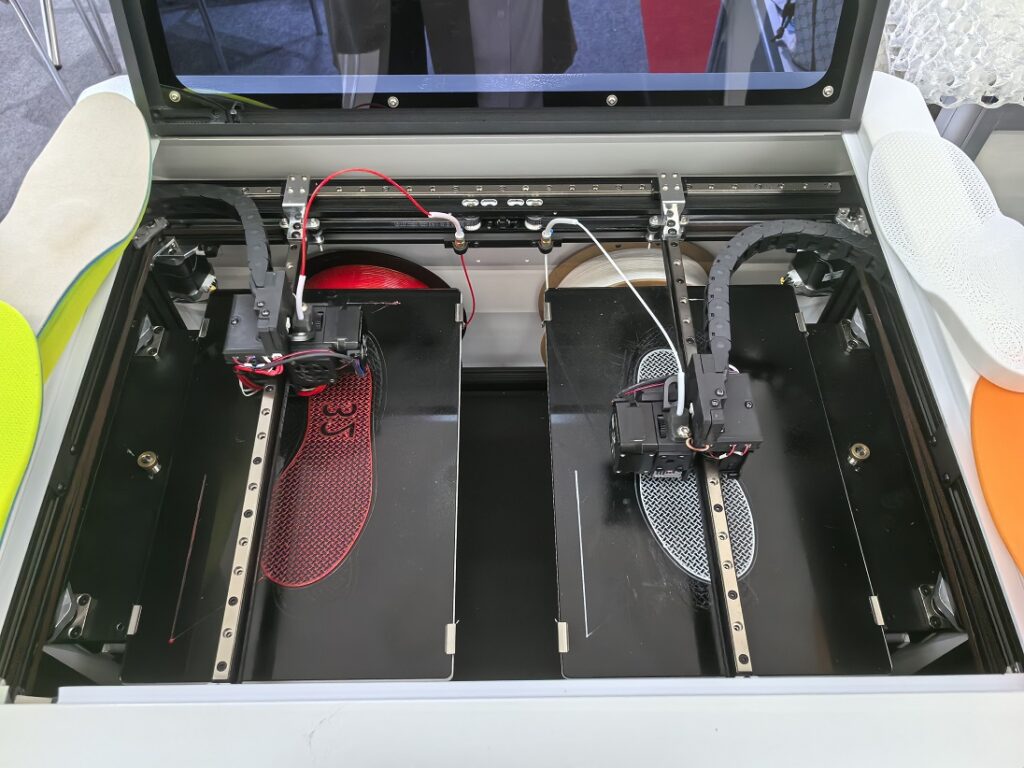
The Advantages of 3D-Printed Insoles in Clinical Practice
Unmatched Precision
Unlike mass-produced inserts, 3D-printed insoles are mapped exactly to each patient’s anatomical structure. This level of customization improves pressure redistribution, enhances stability, and reduces pain more effectively.
Durability Through Materials
Modern 3D printing materials are engineered for long-term use, combining flexibility and strength. Whether the patient is walking all day or training athletically, these insoles maintain performance over time.
Scalable and Efficient Production
What once took days or weeks can now be accomplished in hours. The streamlined digital workflow—from scan to print—reduces production times without sacrificing customization. Clinics can now offer same-day or next-day custom insole solutions.
Cost Efficiency at Scale
Thanks to OEM production systems like PioCreat, large-scale manufacturing of personalized insoles becomes feasible. This reduces per-unit cost, allowing practices to deliver premium products at a competitive price.
The Technology Behind the Solution
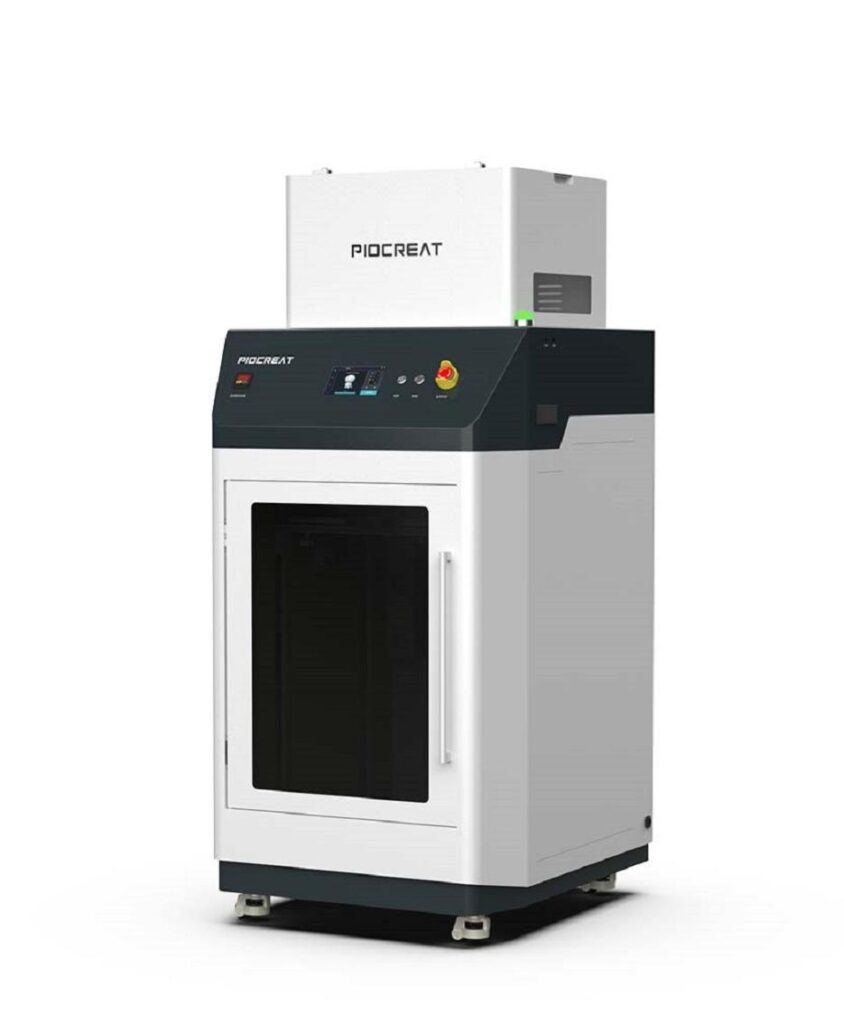
IPX2 FDM 3D Printer
The IPX2 isn’t just another desktop printer—it’s purpose-built for orthotic insole production. With independent dual extruders, it supports simultaneous printing of multiple material types, making it possible to create insoles with both soft zones and rigid frames in a single print.
Other key features:
Designed for flexible materials
Easy-to-use interface for clinical staff
Fast turnaround for high patient volume environments
This printer helps podiatrists and orthotic technologists scale up in-house production, reduce outsourcing costs, and maintain full control over customization.
FS A003 Smart Foot Scanner
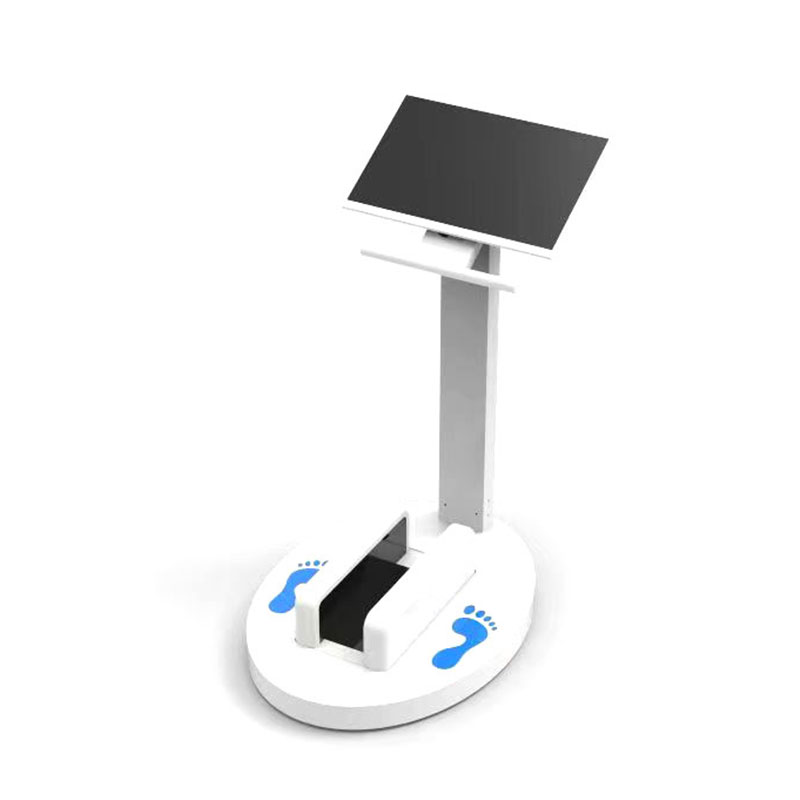

The FS A003 offers a compact, high-speed scanning system with full 3D modeling capabilities:
Millimeter-level precision
5–10 second scan time
Seamless integration with CAD/CAM design software
It’s optimized for clinics that need consistent, high-fidelity data capture for orthotic production.
FS B001 Portable Scanner
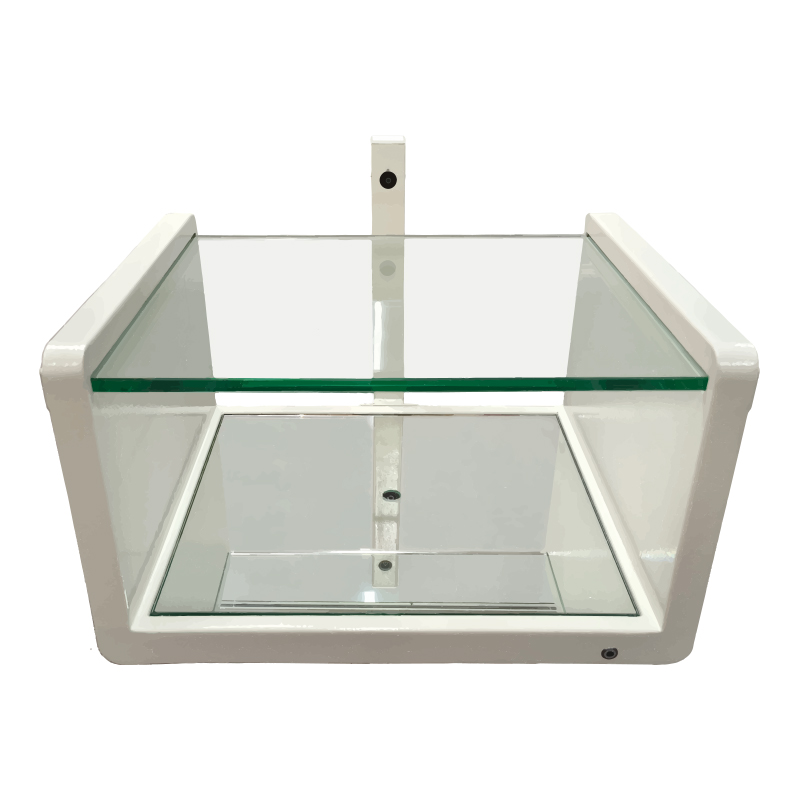

Designed for rapid scanning in dynamic environments, the FS B001 delivers:
±2–3mm accuracy
1.5-second scanning time
Intelligent reporting on arch type, heel angle, foot length, and more
Its speed and portability make it especially useful for pediatric assessments, home visits, or sports medicine applications.
Real-World Impact
For prosthetists, orthotists, and orthopedic manufacturers, adopting a 3D printing insole solution is more than a tech upgrade—it’s a strategic shift. By combining smart scanning, AI-informed design, and additive manufacturing, practitioners gain the ability to:
Improve patient outcomes through precision-fit support
Reduce lead times and cost per unit
Eliminate inconsistencies in manual fabrication
Offer new services like same-day orthotic delivery
Expand business models into sports, rehabilitation, and wellness markets
Conclusion
3D printing isn’t just the future of orthotic insoles—it’s the present. With integrated systems like the IPX2 printer and FS series scanners, medical device professionals can deliver highly customized, clinically effective insoles at scale. For clinics and manufacturers looking to increase efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance patient satisfaction, 3D-printed insole solutions represent a clear path forward.
Ready to evolve your orthotics practice? Now is the time to step into the future—one perfectly printed insole at a time.